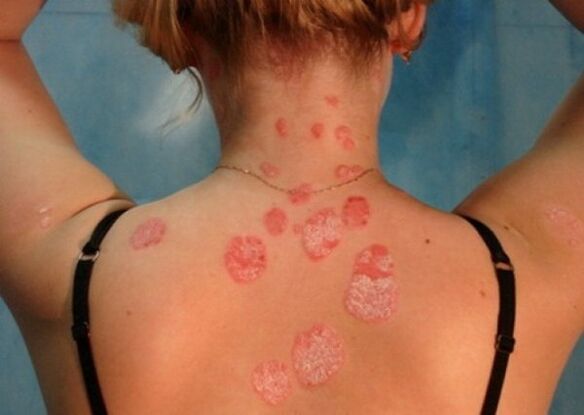
Psoriasis (also known as lichen squamous) is a non-infectious, often recurring, chronic skin disease.
Psoriasis, whose symptoms determine its tendency to damage periarticular tissues, manifests itself in the form of scaly papules, in addition, it is worth noting that this disease is one of the most common skin lesions that occurs at any age.
The etiology of this disease has not yet been fully studied and proven, however, many dermatologists still agree that psoriasis is a disease directly related to hereditary genetic pathologies.
Don't self-medicate. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor.
general description
Psoriasis is characterized by the duration and persistence of its own course. Its remissions, which may last several months or several years, however, indicate its subsequent return and lifetime duration. Spontaneous cure of this disease is extremely rare.
If you try to determine a specific category of people predisposed to the onset of psoriasis, the solution is not unambiguous. The fact is that psoriasis, acting as a systemic process, develops not only in people with real immunological disorders, but also in people who have certain functional or morphological disorders associated with the functions of various systems and organs.
Belonging to the group of dermatoses, psoriasis is one of the most studied diseases in them. However, none of the hypotheses that exist today can fully determine the essence of this disease. Given this, the problems associated with its therapy and prevention are in the same uncertain and, at the same time, acute situation as they were before. Depending on the specific time period, various ideas have been proposed about the origin of psoriasis. This, in turn, led to the selection of several forms, each based on the results of certain laboratory studies and clinical observations.
- The hereditary nature of the disease. This implies the presence of psoriasis in the framework of consideration of several generations, in which, therefore, cases of this disease were observed. By the way, it is heredity that is considered practically the main and reliable cause of the development of psoriasis (in this case, psoriasis increases under the influence of various types of triggering factors).
- The metabolic nature of the disease. In this case, disorders in fat metabolism (i. e. cholesterol metabolism), reduced morbidity during periods of famine, increased amount of phosphorus in the psoriatic scales, etc. , are considered.
- The viral nature of the disease. In this case, the concept of the direct involvement of a viral infection in the etiology of the disease in question was formed on the basis of numerous long-term clinical observations. So, for the same reason, the infectious (and viral) nature as a theory of psoriasis development is the oldest. Thus, the end of the 19th century was marked by cases of formation of very extensive groups of psoriatic-type formations, formed in the context of patients suffering from diseases such as scarlet fever and influenza. The systemic nature of the actual lesion, its recurrent and prolonged course, the presence of a connection with meteorological and heliophysical factors, as well as certain characteristics inherent in the evolution of the characteristic rashes of psoriasis, also acted as confirmation of the infectious nature of the disease. disease. As for timing, a search is now underway for those viral agents through which the psoriatic process can be triggered.
- Endocrine nature of the disease. The theory of a direct connection between the onset of psoriasis and the endocrine (as well as metabolic) nature in the recent past has been supported by many. When examining patients with psoriasis, certain disorders of the endocrine scale were revealed quite often, which served as a justification for the relevance of such a connection. In particular, disorders associated with the functional state inherent in the sex glands, the influence caused by the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, childbirth and lactation, the pronounced type of alterations detected in the study of the pituitary-adrenal system of patients were highlighted.
- The neurogenic nature of the disease. It consists of the onset of the disease in the context of a nervous shock that is real for the patient (more precisely, after the transference). In about 30% of cases, the exacerbation of the disease occurs precisely on the basis of stress. In this case, patients have a reduced ability to withstand the impact of stress and the subsequent transfer of its consequences. At the same time, the disorders they have (asthenic, vegetative-vascular-visceral, vegetative-vascular-dystonic and asthenodepressive) in combination with neurotic reactions provoke the formation or even exacerbate the characteristics of the prevailing vicious circle.
Classification
As we have already noted, psoriasis acts as a chronic and recurrent disease. Any of its existing forms can be attributed to one of the variants of the relevant classification for psoriasis, in which there is a distribution for pustular or non-pustular psoriasis. In general, the classification is as follows:
- pustular psoriasis
- generalized psoriasis;
- annular psoriasis (annular pustulosis);
- palmoplantar psoriasis (psoriasis of the extremities, persistent palmoplantar pustulosis, pustular psoriasis barbera);
- chronic form of persistent acrodermatitis (psoriasis of the soles of the feet and palms of the hands, palmoplantar psoriasis);
- herpetiform psoriatic impetigo.
- Non-pustular psoriasis
- psoriasis vulgaris or psoriasis vulgaris, simple psoriasis (plaque, stable psoriasis in the chronic form);
- psoriatic erythroderma (erythrodermic psoriasis).
Several authors adhere to the need to complement this classification, due to which types or forms of psoriasis can be added to it in the following variants:
- seborrhea-like psoriasis (seborrhea psoriasis);
- napkin psoriasis;
- drug-induced psoriasis;
- "Reversible psoriasis" (psoriasis of skin folds, flexor surfaces).
Psoriasis: symptoms
The first symptoms of psoriasis are the eruption of miliary papules, characterized by a gradual increase along the periphery, at the same time they transform into nummular and lenticular papules and merge with each other, due to which plaques appear. many sizes. The development of psoriasis on the skin defines three main stages for it.
First step
This stage is defined as a progressive stage, it is caused by the formation of new formations on the skin (actually papules) as well as an increase in the size of formations that are already on the skin. This is also accompanied by the formation of an erythematous border around the lesions (such a border is defined as a zone of peripheral growth). Plaque along the edges is not susceptible to desquamation, while desquamation, acting as a final stage of inflammation, does not accompany the process of growth of psoriatic formations.
second stage
The second stage defines a stationary period in which new elements do not appear, however, the existing elements in the form of plaques and papules do not change in size. In general, the appearance of papules can be completed at any stage, therefore, the stationary period may be accompanied by the simultaneous appearance of miliary, lenticular and nummular papules. We will explain what are the three listed types of papules. Thus, nummular papules are elements of a rash rounded in diameter from 15 to 20 mm (for this reason, these papules are also called coin-shaped). Lenticular papules, in turn, are elements of a rash, flat or convex, oval or rounded, resembling lentils. And finally, miliary papules, which have a conical shape of elements and are therefore similar to hemp seed. Basically, these papules are small in size, the predominant area is close to the hair follicles.
third stage
This stage is reversed (or regressive). Its main feature is that the eruptions gradually disappear and a whitish border of a pseudosclerotic type is formed around the foci themselves (it is defined as the Voronov border). During this period, some patients may experience mild itching. As for any subjective sensations, they are mostly insignificantly expressed, or even completely absent.
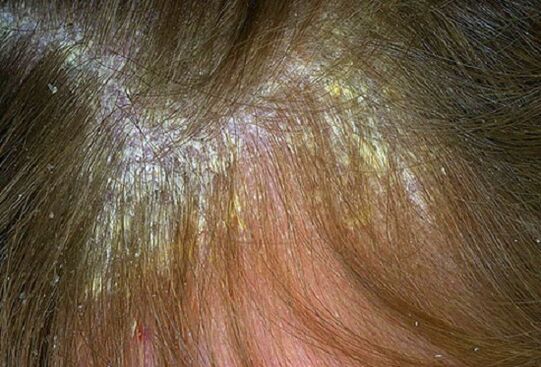
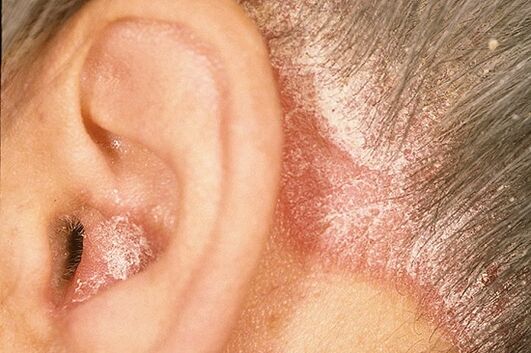
The appearance of rashes can be observed on any area of the skin, however, they are predominantly located in the area of the surface of the folds of the limbs, in particular on the elbow and knee joints, in the sacrum region, the scalp (here, in particular, the area along the edge of the hair growth, defined as the "psoriatic crown") is distinguished. Psoriasis on the head, the symptoms of which, although determined by the severity of its own manifestations, do not lead to a change in the structure of the hair, as well as its loss.
As for the concentration of plaques on the extensor surface of the knee and elbow joints, here they usually persist for a long period of time from the moment the rash disappears in general (this feature defines them as "duty" plaques). Some patients are faced with the fact that the skin folds in the inguinal-femoral region or in the mammary glands as well as in the axillary glands are affected, and often this lesion can be isolated.
irritated psoriasis
It develops against the background of active exposure of the skin with an already existing progressive psoriasis from certain irritants, in particular, the sun's rays or specific ointments, as well as other types of irritants that affect plaques. These plates, in turn, become more convex, the color changes to cherry red, a hyperthermal belt forms in the surrounding area, due to which the sharp boundaries become a little blurred. This belt, following the resolution of the plate, takes on a wrinkled appearance.
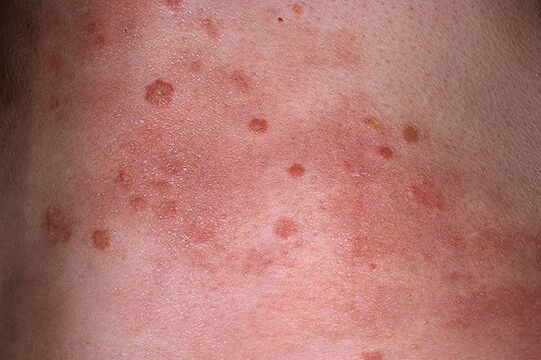
spotted psoriasis
This form of the disease manifests itself in the form of mild infiltration (in the general definition, infiltration is the impregnation of tissues with one or another substance) of the elements of the eruption. They, in turn, look like spots (not papules). Spotty psoriasis develops, as a rule, acutely and is also characterized by a resemblance to toxidermia. As the main method in differentiating the disease, the definition of the correspondence of the course of the disease with its characteristic psoriatic triad is used.
old psoriasis
This form of the disease can be considered in terms of symptoms in the form of severe infiltration on the side of the plaques, its general cyanosis, with a hyperkeratotic or verrucous surface. This type of outbreak is especially difficult to cure, and its transformation in the future into a malignant tumor formation is not excluded (this happens infrequently, but, unfortunately, it is not necessary to exclude this option).
seborrheic psoriasis
This form of psoriasis, as its name suggests, develops in patients with seborrhea that is already relevant to them. The disease manifests itself on the scalp, in the area behind the auricles, on the chest, in the area of the nasolabial folds, in the subscapular and scapular parts of the back. Emerging psoriatic scales are subject to intense sebum saturation, so they adhere and remain on the surfaces of the plaque, which allows the disease to simulate a characteristic picture of seborrheic eczema.
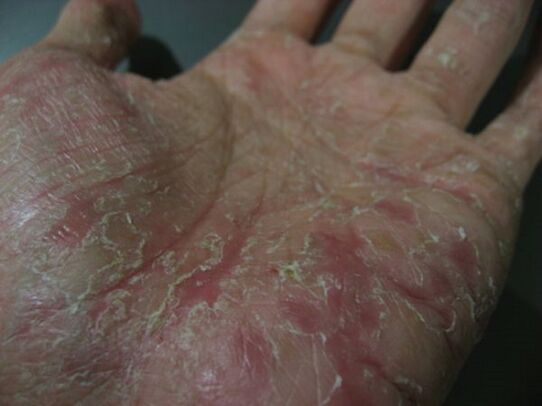
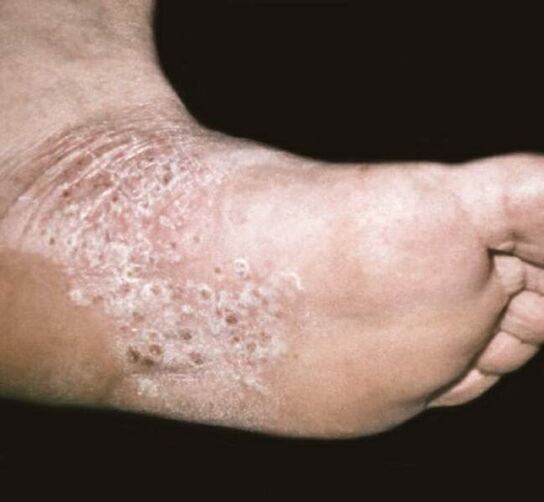
Palmar-plantar psoriasis
The disease can manifest itself either in the form of common psoriatic plaques and papules, or in the form of hyperkeratotic formations that simulate corns and calluses. In some cases, psoriasis on the hands, the symptoms of which are observed in this case on the palms of the hands (or on the legs - according to the definition, on the soles) is continuous, which manifests itself in the form of increased thickening or keratinization . The limits of this type of injury are characterized by clarity; in rarer cases, this form of psoriasis is limited to the appearance of large rings of desquamation.
exudative psoriasis
This form of psoriasis is characterized by excessive severity of exudate during an inflammatory reaction; appears within the progressive period of the course of psoriasis. Arriving at the surface of the papule, the exudate provides the saturation of the accumulation of scales, forming from them formations that look like crusts. These elements are secondary, define them as flaky crusts, the color of these elements is yellowish. Upon removal, a slightly bleeding and weeping surface is subject to exposure. Scale crusts, when dry and stratified, often form a massive conglomerate type, resembling an oyster shell (this is already defined as rupioid psoriasis).
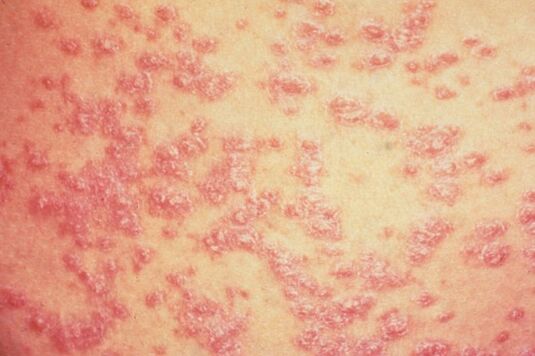
guttate psoriasis
Guttate psoriasis, the symptoms of which appear suddenly, is characterized by the formation of various spots on the skin. Mostly the disease is diagnosed in patients aged between 8 to 16 years. Streptococcal infection often acts as a precursor to teardrop-shaped psoriasis.
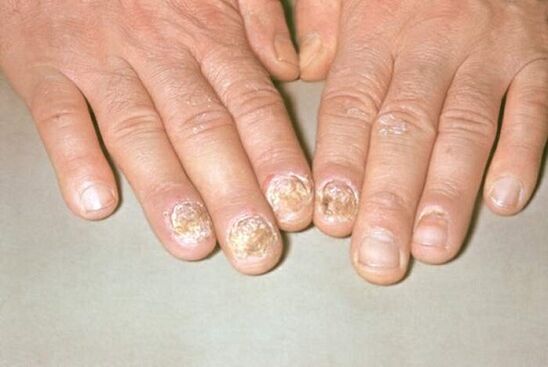
nail psoriasis
Nail psoriasis, whose symptoms provide isolation of this type of psoriasis in three main forms, depending on the degree of nail damage, can be atrophic, punctual or hypertrophic.
A punctate lesion is the formation of punctate depressions in the nail plates, which can also be compared to the surface of a thimble. The manifestation of this form of psoriasis is possible in a slightly different version, which, in its specificity, is similar to onychomycosis. In this case, within the free edge, the nail plate changes color, becomes opaque, prone to crumbling without much effort. As a sign that allows you to differentiate psoriasis, an inflammatory border formed along the periphery of the affected nail plate area is determined. It appears as the edge of a papule within the nail bed, visible through the nail plate.
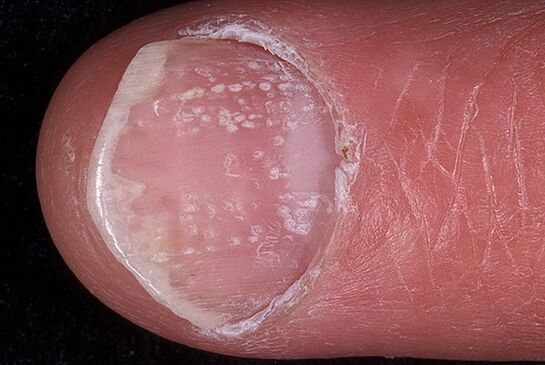
Psoriatic arthritis (psoriasis)
Psoriasis arthritis, the symptoms of which are manifested due to infiltration, relevant to periarticular tissues with simultaneous joint damage, mainly affects the interphalangeal joints. Meanwhile, the possibility of involvement of large joints in the pathological process is not excluded; the joints and joints of the sacroiliac spine are extremely rarely at risk in this regard.
It is important to take into account that psoriatic arthritis, unlike other types of arthritis (which in the general definition means inflammation of the joints), is formed against the background of a psoriatic rash that already exists in the patient, often combined with nail damage. Furthermore, an important point can be made that the onset of this type of arthritis is combined with an exacerbation of psoriasis on the skin, which, in most cases, acquires an exudative character.
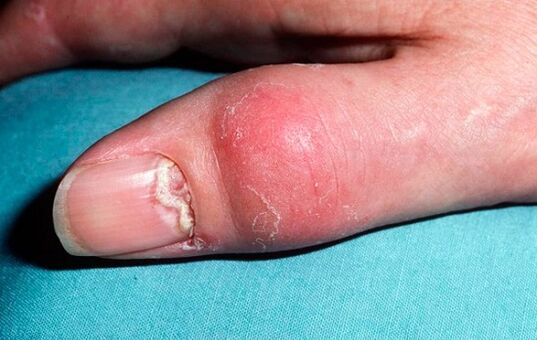
Irrational treatment of the disease during the period of its progression is often accompanied by the occurrence of a nonspecific reaction of the body. It is toxic-allergic in nature and consists of the appearance of redness in the area of areas not affected by psoriatic plaques, this redness, merging, completely affects the skin. This process is combined with a high temperature (within a range of not more than 39 degrees), as well as an increase in lymph nodes, a feeling of tight, burning and itchy skin. In frequent cases, there is also profuse peeling, thickening and exfoliation of the nail plates, hair loss. This picture already indicates the relevance of psoriatic erythroderma. Erythroderma ends with the restoration of the traditional version of the course of psoriasis.
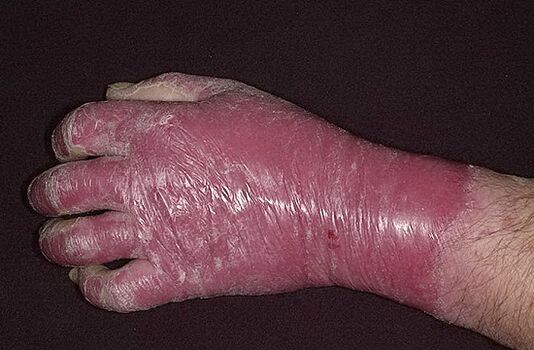
In general, recurrence of the disease occurs in autumn-winter, as well as in spring-summer periods, which is an important factor that needs to be taken into account, including when prescribing the necessary treatment.
Psoriasis treatment
Before appointment of treatment, a thorough examination of the patient is carried out, and already to determine specific measures, they are based on the stage of the course of the disease, its clinical variety, the general condition of the patient, the presence of concomitant diseases, compliance from disease manifestations to seasonality, etc. the fastest and at the same time a favorable treatment result is achieved in the case of uncomplicated forms of psoriasis with its short course, as well as limited manifestations. In general, the treatment of psoriasis is a rather laborious process, and in most cases it is not possible to obtain a complete cure - the disease simply regresses (that is, it begins a period of its existence without symptoms), which, however, , is also a positive result for him.
The main goal in treatment was determined to be the maximum possible suppression of symptoms in combination with the addition of preventive measures.
First of all, with psoriasis, a diet is prescribed, in which foods that provoke an exacerbation of the disease (spicy foods, chocolate, alcoholic beverages) are excluded from the diet. The restriction also applies to consumption of smoked meats, honey, fried and fatty foods, etc. During the period of exacerbation of the course of the disease, it is recommended to eat more fruits and vegetables (with the exception of red: apples, tomatoes, cherries, etc. ), fish and lean (cooked) meats.
The course of psoriasis has a beneficial effect on its treatment in the conditions of the sanitary facilities of the spas. Taking into account the special susceptibility of the skin in patients with psoriasis, it is recommended to avoid sun exposure for 11 to 16 hours.
As for the drug treatment of psoriasis, it is based on the use of various methods. Firstly, there are external agents (creams, ointments, etc. ), systemic treatment medications (injections, pills, etc. ) and methods such as phytochemotherapy (phytotherapy), physical therapy, etc. external treatment methods. In particular, the following drugs were most commonly used among them:
- Salicylic ointment. With its help, the softening of the formed scales is guaranteed, which, in turn, provides the possibility of their early elimination, together with a better absorption of another type of drug. This ointment (0, 5% or 5%) is applied to the affected areas of the skin in a thin layer, 1-2 times a day. An important feature of the application is the use of a smaller amount of ointment with a significant nature of inflammation (that is, the more inflammation is more pronounced in the nature of its manifestation, the less amount of ointment is used for it, respectively). Salicylic acid, which acts as the base of the medication, is also found in several other ointments used to treat psoriasis.
- Sulfur tar ointment (5 or 10%). The use of this ointment provides a reduction of inflammatory processes relevant to the skin. The contraindication for use is exudative psoriasis (ie psoriasis, accompanied by weeping crusts and scales). You cannot apply this ointment on the skin of the face. Tar shampoos are used to treat scalp psoriasis.
- Naphthalene ointment. It is used to treat the regressive and stationary stages of the disease. The exacerbation or progression of psoriasis determines the inadmissibility of the use of this remedy. With the help of this ointment, severe itching and inflammation are reduced. A 5% or 10% ointment is used.
- Glucocorticosteroid drugs. Its use provides a decrease in the intensity of inflammation. They are only used in short-term courses, with mandatory expert supervision.
- Ointments containing vitamin D. Such ointments provide an anti-inflammatory effect, while at the same time improving the course of the disease.
As for systemic treatment, it is selected strictly individually and only by the attending physician. As already noted, it means the use of various pills, injections, etc.
Phytochemotherapy as a method of treating psoriasis consists of ultraviolet exposure of the affected areas of the skin. For this, a special type of installation is used, which radiates these areas without affecting healthy skin.
In general, the treatment of psoriasis can mean many different regimens implemented in practice, but none of these regimens is generally accepted due to the difference in their course and specificity, so the effectiveness of any one regimen cannot be determined equally for all patients. . We repeat that the treatment of the disease is carried out strictly on an individual basis, under the constant supervision of the attending physician.
If symptoms that indicate psoriasis appear, it is necessary to contact a dermatologist and an infectious disease specialist.























